Презентація на тему:
Доклад С-реактивный белок
Завантажити презентацію
Доклад С-реактивный белок
Завантажити презентаціюПрезентація по слайдам:
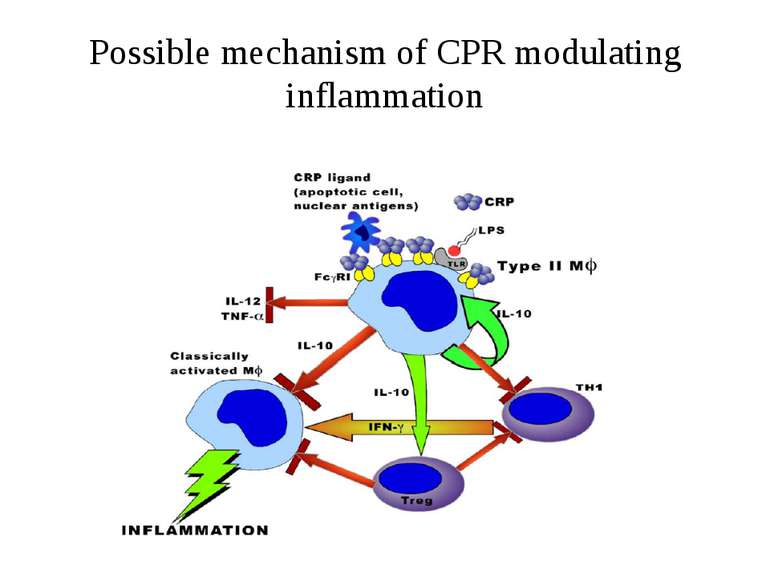
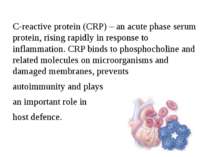
C-reactive protein (CRP) – an acute phase serum protein, rising rapidly in response to inflammation. CRP binds to phosphocholine and related molecules on microorganisms and damaged membranes, prevents autoimmunity and plays an important role in host defence.
CRP was first detected in 1930 by Tillet and Frances, who detected a substance in the sera of patients with Streptococcus pneumoniae infection that formed a precipitate when combined with polysaccharide C of the cell wall of the pneumococcus and they called it C-reactive substance, which was later changed to C-reactive protein.
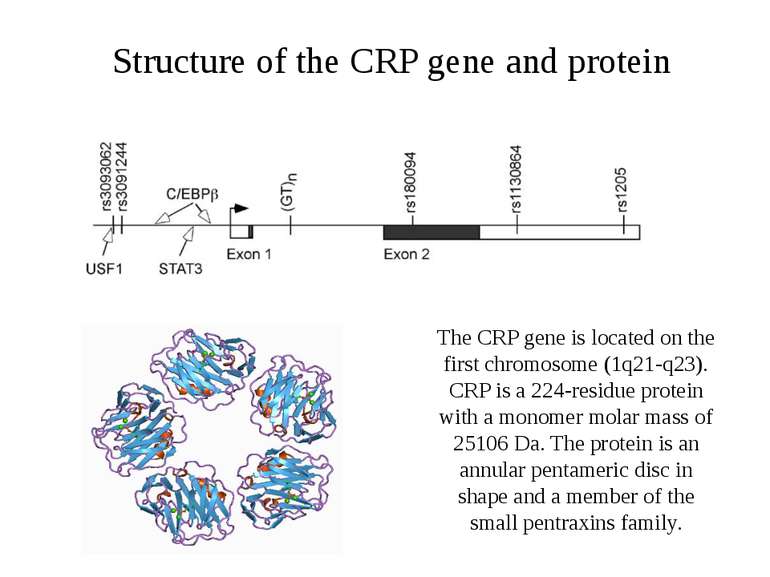
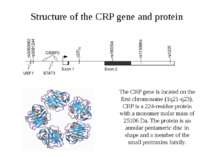
Structure of the CRP gene and protein The CRP gene is located on the first chromosome (1q21-q23). CRP is a 224-residue protein with a monomer molar mass of 25106 Da. The protein is an annular pentameric disc in shape and a member of the small pentraxins family.
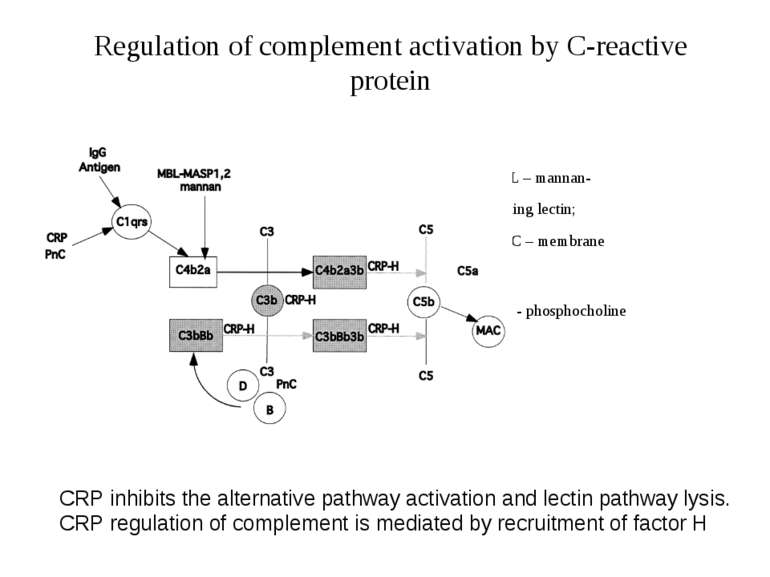
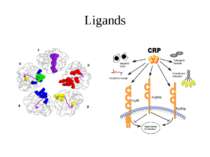
Regulation of complement activation by C-reactive protein MBL – mannan- b binding lectin; MAC – membrane attack complex; attack complex; PnC - phosphocholine CRP inhibits the alternative pathway activation and lectin pathway lysis. CRP regulation of complement is mediated by recruitment of factor H
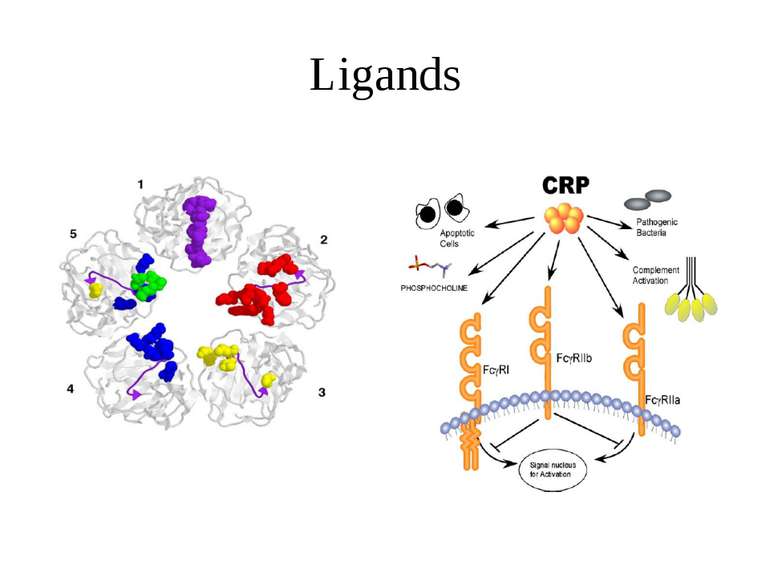
Binding to receptors The binding of CRP to receptor is expected to have similar effects as the binding of IgG. The complex activates several cascades of events: – Activation of the PI-3K pathway – Activation of the ERK1/2 cascade (IL-8 synthesis, MMP-1 secretion) – Inducing of the phospholipase D activity
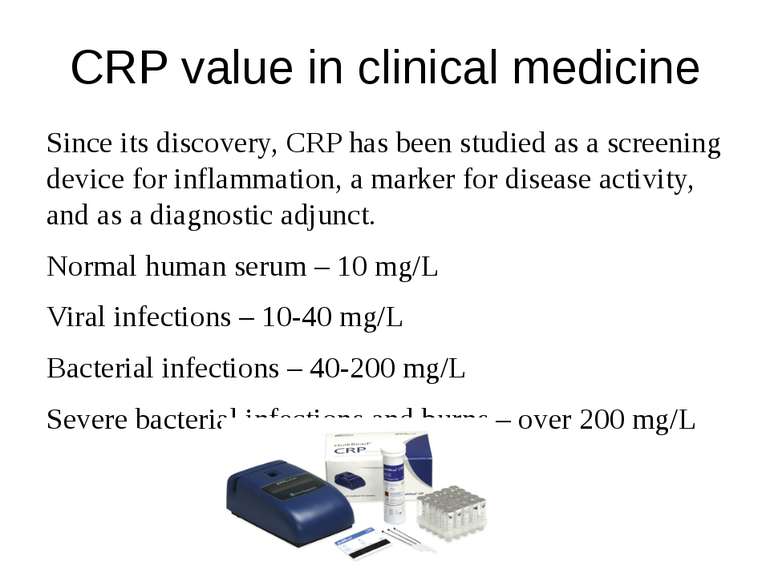
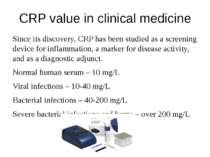
CRP value in clinical medicine Since its discovery, CRP has been studied as a screening device for inflammation, a marker for disease activity, and as a diagnostic adjunct. Normal human serum – 10 mg/L Viral infections – 10-40 mg/L Bacterial infections – 40-200 mg/L Severe bacterial infections and burns – over 200 mg/L
A positive CRP may be an indicator of several conditions, including: - Appendicitis - rheumatoid arthritis - Cholecystitis - rheumatic fever - Pancreatitis - cancer - Pelvic inflammatory - tuberculosis disease - heart attack - Pneumonia - lupus - Urinary tract infection - Meningitis - Neonatal sepsis and pediatric infections
C-reactive protein adds little to diagnosis of pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and pancreatitis. False negative CRP results in the setting of meningitis, neonatal sepsis, and bacteremia are common and therefore unhelpful. A single CRP value should not factor into the decision to treat these patients. B.Clyne and J.Olshaker, 1999
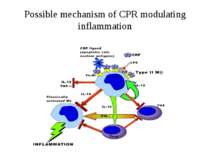
Summary CRP can be both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory and the primary role of CPR is likely to be the regulation of acute inflammation. Unfortunately, the nonspecific nature of the acute phase response prevents CRP from being a useful discriminatory diagnostic test.
Схожі презентації
Категорії