Презентація на тему:
miRNA
Завантажити презентацію
miRNA
Завантажити презентаціюПрезентація по слайдам:
Identified and characterized the first microRNA. Dr. Ambros' laboratory yielded the discovery of the first microRNA Dr. Ruvkun's laboratory identified how that microRNA regulates its target messenger Together, they demonstrated that the microRNA inactivates its target through direct, base-pairing interactions.
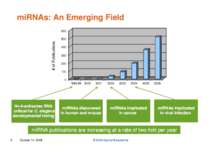
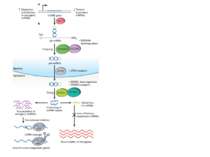
miRNA 1. More than 1000 miRNAs are encoded in the human (2% of all mammalian genes) ONE miRNA is able to regulate the expression of tens to hundreds of different genes miRNAs can function as “master-switches,” efficiently regulating and coordinating multiple cellular pathways and processes. miRNAs are responsible for: embryonic development immune and related inflammatory responses cellular growth and proliferation 5. Misregulation of miRNAs play a fundamental role in the; Growth and dissemination of many cancers Eye and retina disoders Kidney disorders Viral infection
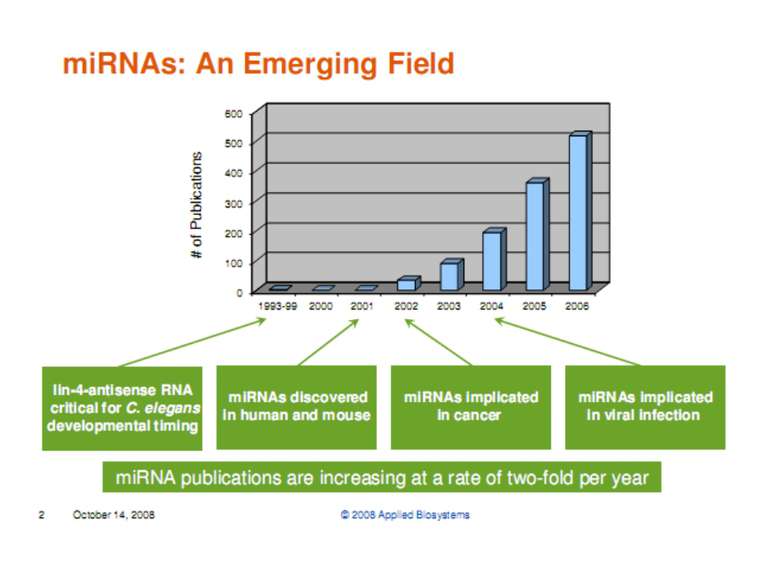
DATABASE: When RNA Says No Small strands of RNA that stifle protein synthesis are one of the hottest topics in molecular biology because they might be able to stem cancer and other diseases. Researchers looking for information on one type of obstructionist RNA, called microRNA (miRNA), should check out the miRNA Registry from the Sanger Institute in Hinxton, U.K. The site tallies sequence data on more than 700 miRNAs from eight species, including humans. You can also locate the original literature description and similar miRNAs. To help the field keep miRNA nomenclature straight, researchers can deposit a newly discovered sequence, and the curators will name it. Science 19 March 2004: Vol. 303 no. 5665 p. 1741 miRBase 19 released (1 August 2012) miRBase 19 is now available, brought to you from the Benasque RNA meeting in the sunny Pyrenees, and with a slightly larger time gap than usual. In that extended time, we have added more than the usual number of new sequences — 3171 new hairpins and 3625 novel mature products, bringing the totals to 21264 miRNAs
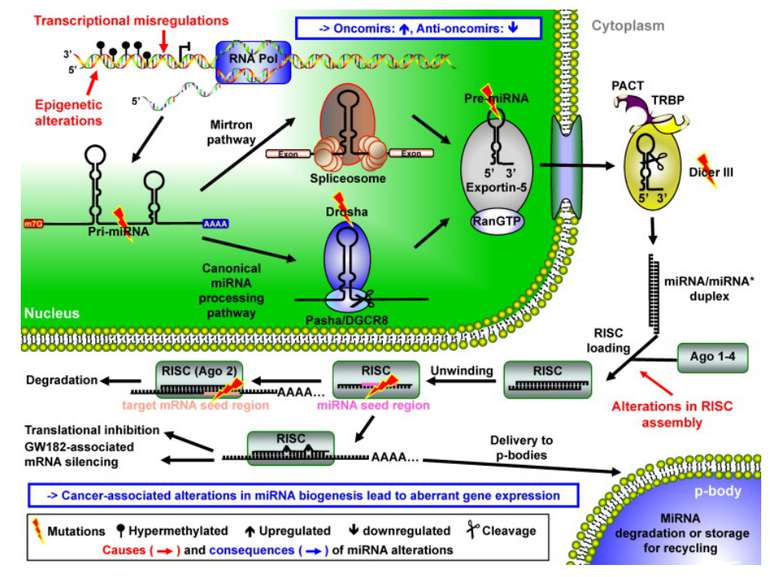
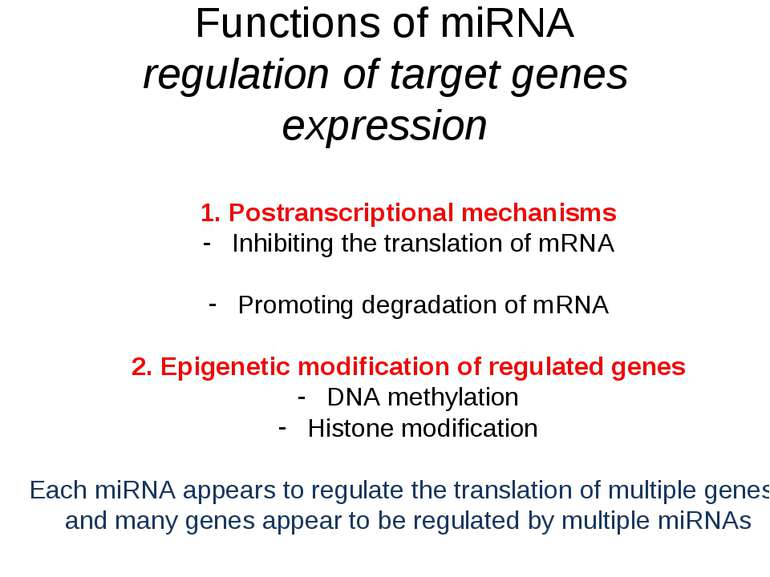
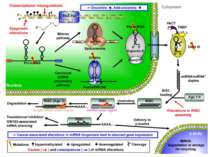
Functions of miRNA regulation of target genes expression Postranscriptional mechanisms Inhibiting the translation of mRNA Promoting degradation of mRNA Epigenetic modification of regulated genes DNA methylation Histone modification Each miRNA appears to regulate the translation of multiple genes, and many genes appear to be regulated by multiple miRNAs
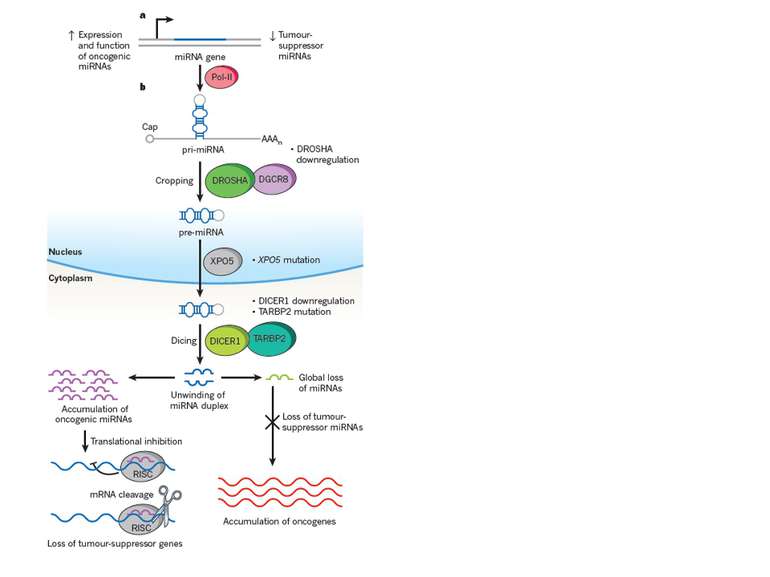
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Mar 2;101(9):2999-3004. Epub 2004 Feb 18. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M, Croce CM. The microcosmos of cancer Nature 482, 347–355 (16 February 2012)
Applications of miRNA therapeutic and diagnostic options The special features of miRNAs make them potentially useful for detection in clinical specimens relatively resistant to ribonuclease degradation can be easily extracted from small biopsies, frozen samples and even formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues relatively simple and reproducible assays have been developed to detect the abundance of individual miRNAs methods that combine small RNA isolation, PCR and next-generation sequencing, allow accurate and quantitative assessment of all the miRNAs that are expressed in a patient specimen, including material that has been isolated by laser capture microdissection.
Applications of miRNA therapeutic and diagnostic options Potential use of miRNA mimics or antagonists as therapeutics A) the targeting of a single miRNA can be a form of 'combination' therapy B) because miRNA expression is often altered in cancer cells, agents that modulate miRNA activity could potentially produce cancer-specific effects C) anticancer therapies that inhibit or enhance miRNA activity are being developed (based on animal study) Oncogenic miRNAs can be blocked by: antisense oligonucleotides antagomirs sponges locked nucleic acid (LNA) constructs
- MRX34 is the first of a series of clinical therapeutic candidates from Mirna Therapeutics - Designed to mimic the activity of a human microRNA-34 - MRX34 is a liposome-formulated mimic of the tumor suppressor miR-34 - miR-34 is lost or expressed at reduced levels in most solid and hematologic malignancies miR-34 functions within the p53 pathway and inhibits cancer cell growth by repressing MYC, MET, BCL2, β-catenin, and other oncogenes MRX34 induces cell cycle arrest, senescence and apoptosis, interferes with the viability of cancer stem cells, creates a barrier to metastasis, and abolishes chemoresistance
Santaris Pharma A/S advances MIRAVIRSEN, the first microRNA-targeted drug to enter clinical trials, into Phase 2 to treat patients infected with Hepatitis C virus - Santaris Pharma A/S initiates Phase 2a clinical trial with miravirsen (SPC3649) to assess safety and tolerability in treatment-naïve patients with chronic Hepatitis C Miravirsen is the first microRNA-targeted drug to receive Investigational New Drug (IND) acceptance from FDA, paving the way to conduct Phase 2 trials for treatment of Hepatitis C in the United States The Phase 2a clinical trials will be conducted in the Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Romania, and Slovakia. - Developed using Santaris Pharma A/S Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) Drug Platform, miravirsen inhibits miR-122, a microRNA important for Hepatitis C viral replication, thereby significantly reducing the levels of Hepatitis C virus - Due to unique mechanism-of-action, miravirsen holds promise as new treatment option for Hepatitis C patients, including the 50% of patients not responsive to current standard of care1
Схожі презентації
Категорії