Презентація на тему:
Computer
Завантажити презентацію
Computer
Завантажити презентаціюПрезентація по слайдам:
Capabilities of computers (In general) 1.) Ability to perform certain logical and mathematical functions. 2.) Ability to store data and/or information. 3.) Ability to retrieve data and/or information. 4.) Ability to search data and/or information. 5.) Ability to compare data and/or information. 6.) Ability to sort data and/or information. 7.) Ability to control errors. 8.) Ability to check itself. 9.) Ability to perform a set of tasks with speed and accuracy. 10.) Ability to do a set of tasks repetitively. 11.) Ability to provide new time dimensions. 12.) Excellent substitute for writing instrument and paper. Limitations of computers (In general) 1.) Dependence on prepared set of instructions. 2.) Inability to derive meanings from objects. 3.) Inability to generate data and/or information on its own. 4.) Cannot correct wrong instructions. 5.) Dependence on electricity. 6.) Dependence on human interventions. 7.) Inability to decide on its own. 8.) Not maintenance-free. 9.) Limited to the processing speed of its interconnected peripherals. 10.) Limited to the available amount of storage on primary data storage devices. 11.) Limited to the available amount of storage on secondary data storage devices. 12.) Not a long-term investment. About the capabilities and limitations of computers
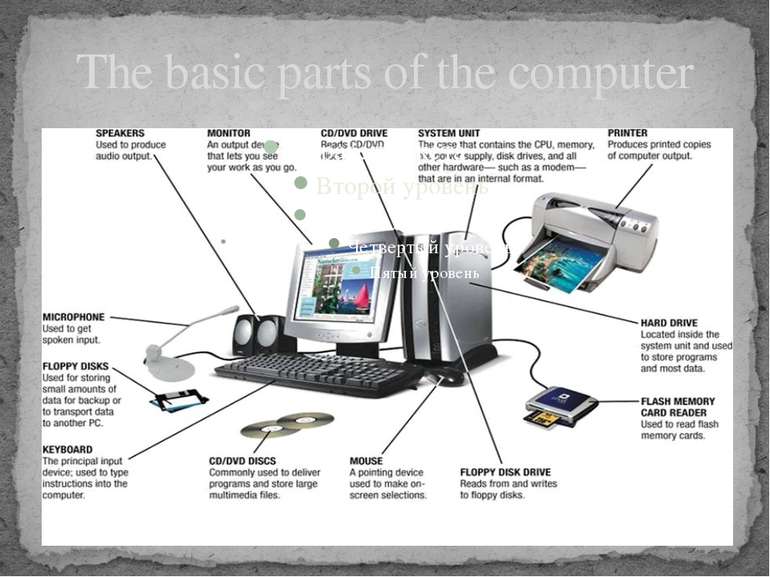
About a computer case A computer case also known as a "computer chassis", "tower", "system unit", "base unit" or simply "case" and sometimes incorrectly referred to as the "CPU" or "hard drive", is the enclosure that contains most of the components of a computer (usually excluding the display, keyboard and mouse). Cases are usually constructed from steel (often SECC — Steel, electrogalvanized, cold-rolled, coil) or aluminium. Plastic is sometimes used, and other materials such as glass,wood and even Lego blocks have appeared in home-built cases.
About a CD Compact disc, or CD for short, is a digital optical disc data storage format. The format was originally developed to store and play back sound recordings only (CD-DA), but was later adapted for storage of data (CD-ROM). Several other formats were further derived from these, including write-once audio and data storage (CD-R), rewritable media (CD-RW), Video Compact Disc (VCD), Super Video Compact Disc (SVCD), Photo CD, PictureCD, CD-i, and Enhanced Music CD. Audio CDs and audio CD players have been commercially available since October 1982. Standard CDs have a diameter of 120 millimetres (4.7 in) and can hold up to about 80 minutes of uncompressed audio or 700 MiB (actually about 703 MiB or 737 MB) of data. The Mini CD has various diameters ranging from 60 to 80 millimetres (2.4 to 3.1 in); they are sometimes used for CD singles, storing up to 24 minutes of audio or delivering device drivers. At the time of the technology's introduction it had much greater capacity than computerhard drives common at the time. The reverse is now true, with hard drives far exceeding the capacity of CDs. In 2004, worldwide sales of CD audio, CD-ROM, and CD-R reached about 30 billion discs. By 2007, 200 billion CDs had been sold worldwide. Compact discs are increasingly being replaced or supplemented by other forms of digital distribution and storage, such as downloading and flash drives, with audio CD sales dropping nearly 50% from their peak in 2000.
About a CD-ROM Drive CD-ROM discs are read using CD-ROM drives. A CD-ROM drive may be connected to the computer via an IDE (ATA), SCSI, SATA, FireWire, or USB interface or a proprietary interface, such as the Panasonic CD interface. Virtually all modern CD-ROM drives can also play audio CDs (as well as Video CDs and other data standards) when used in conjunction with the right software.
About a floppy disk A floppy disk, or diskette, is a disk storage medium composed of a disk of thin and flexible magnetic storage medium, sealed in a rectangular plastic carrier lined with fabric that removes dust particles. Floppy disks are read and written by a floppy disk drive(FDD). Floppy disks, initially as 8-inch (200 mm) media and later in 5.25-inch (133 mm) and 3.5-inch (90 mm) sizes, were a ubiquitous form of data storage and exchange from the mid-1970s well into the 2000s. By 2010, computer motherboards were rarely manufactured with floppy drive support; 3 1⁄2-inch floppy disks can be used with an external USB floppy disk drive, but USB drives for5 1⁄4-inch, 8-inch and non-standard diskettes are rare or non-existent, and those formats must usually be handled by old equipment. While floppy disk drives still have some limited uses, especially with legacy industrial computer equipment, they have been superseded by data storage methods with much greater capacity, such as USB flash drives, portable external hard disk drives, optical discs,memory cards and computer networks.
About a floppy drive In the early 1980s, a number of manufacturers introduced smaller floppy drives and media in various formats. A consortium of 21 companies eventually settled on a 3 1⁄2-inch floppy disk (actually 90 mm wide), similar to a Sonydesign, but improved to support both single-sided and double-sided media, with formatted capacities of 360 KB and 720 KB respectively. Single-sided drives shipped in 1983,and double sided in 1984. What became the most common format, the double-sided, high-density (HD) 1.44 MB disk drive, shipped in 1986. The first Macintosh computers used single-sided 3.5 inch floppy disks, but with 400 KB formatted capacity. These were followed in 1986 by double-sided 800 KB floppies. The higher capacity was achieved at the same recording density by varying the disk rotation speed with arm position so that the linear speed of the head was closer to constant. Later Macs could also read and write 1.44 MB HD disks in PC format with fixed rotation speed.
About a computer monitor A monitor or a display is an electronic visual display for computers. The monitor comprises the display device, circuitry and an enclosure. The display device in modern monitors is typically a thin film transistor liquid crystal display(TFT-LCD) thin panel, while older monitors used a cathode ray tube (CRT) about as deep as the screen size. Originally, computer monitors were used for data processing while television receivers were used for entertainment. From the 1980s onwards, computers (and their monitors) have been used for both data processing and entertainment, while televisions have implemented some computer functionality. The common aspect ratio of televisions, and then computer monitors, has also changed from 4:3 to 16:9 (and 16:10).
About a mouse(computing) In computing, a mouse is an input device that functions by detecting two-dimensionalmotion relative to its supporting surface. Physically, a mouse consists of an object held under one of the user's hands, with one or more buttons. The mouse sometimes features other elements, such as "wheels", which allow the user to perform various system-dependent operations, or extra buttons or features that can add more control or dimensional input. The mouse's motion typically translates into the motion of a pointer on a display, which allows for fine control of a graphical user interface.
About a computer keyboard In computing, a keyboard is a typewriter-style device, which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys, to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches. Following the decline ofpunch cards and paper tape, interaction via teleprinter-style keyboards became the maininput device for computers. A keyboard typically has characters engraved or printed on the keys and each press of a key typically corresponds to a single written symbol. However, to produce some symbols requires pressing and holding several keys simultaneously or in sequence. While most keyboard keys produce letters, numbers or signs (characters), other keys or simultaneous key presses can produce actions or execute computer commands. Despite the development of alternative input devices, such as the mouse, touchscreen, pen devices, character recognition and voice recognition, the keyboard remains the most commonly used and most versatile device used for direct (human) input into computers.[citation needed] In normal usage, the keyboard is used to type text and numbers into a word processor, text editor or other programs. In a modern computer, the interpretation of key presses is generally left to the software. A computer keyboard distinguishes each physical key from every other and reports all key presses to the controlling software. Keyboards are also used for computer gaming, either with regular keyboards or by using keyboards with special gaming features, which can expedite frequently used keystroke combinations. A keyboard is also used to give commands to the operating system of a computer, such as Windows'Control-Alt-Delete combination, which brings up a task window or shuts down the machine. A command-line interface is a type of user interface operated entirely through a keyboard, or another device performing the function of one.
About a speaker A loudspeaker (or "speaker", or in the early days of radio "loud-speaker") is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signalinput. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful. The most common form of loudspeaker uses a paper cone which is vibrated by an attachedvoice coil electromagnet between the poles of a permanent magnet, but many other types exist. Where high fidelity reproduction of sound is required, multiple loudspeakers may be used, each reproducing a part of the audible frequency range. Miniature loudspeakers are found in devices such as radio and TV receivers, and many forms of music players. Larger loudspeaker systems are used for music, sound reinforcement in theatres and concerts, and in public address systems.
Схожі презентації
Категорії