Презентація на тему:
"The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland"
Завантажити презентацію
"The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland"
Завантажити презентаціюПрезентація по слайдам:
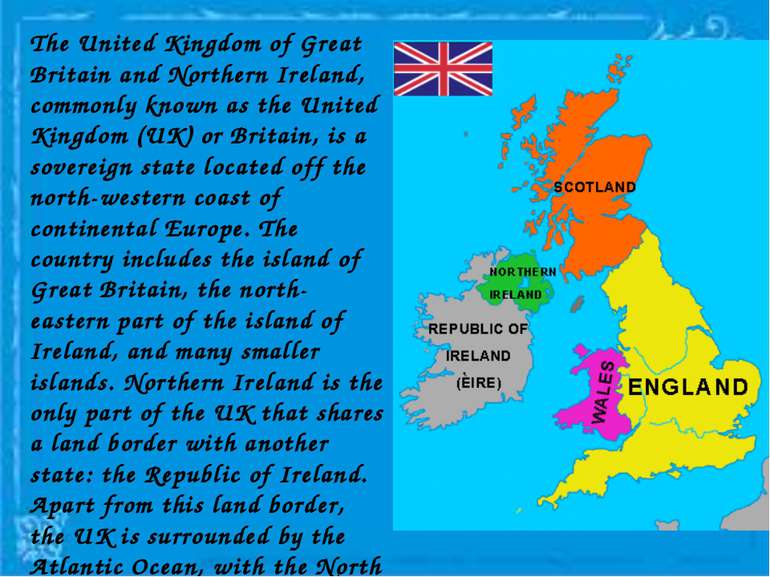
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a sovereign state located off the north-western coast of continental Europe. The country includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands. Northern Ireland is the only part of the UK that shares a land border with another state: the Republic of Ireland. Apart from this land border, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the North Sea in the east, the English Channel in the south and the Irish Sea in the west.
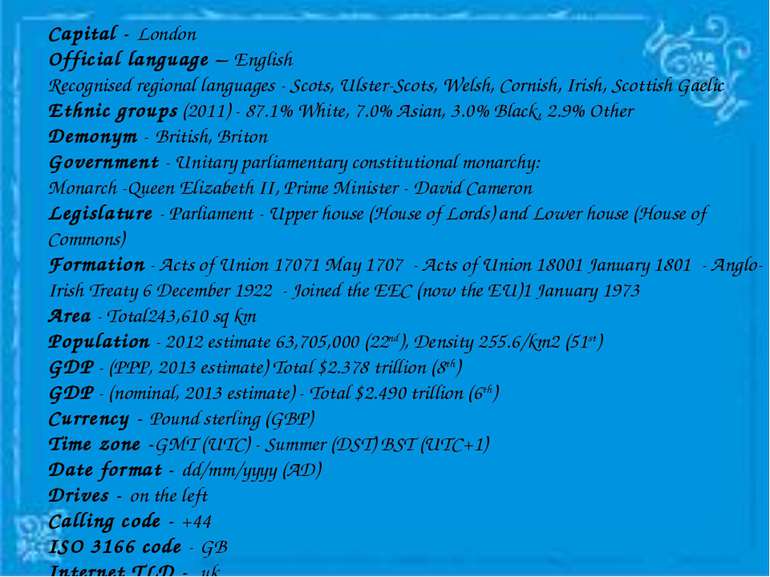
Capital - London Official language – English Recognised regional languages - Scots, Ulster-Scots, Welsh, Cornish, Irish, Scottish Gaelic Ethnic groups (2011) - 87.1% White, 7.0% Asian, 3.0% Black, 2.9% Other Demonym - British, Briton Government - Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy: Monarch -Queen Elizabeth II, Prime Minister - David Cameron Legislature - Parliament - Upper house (House of Lords) and Lower house (House of Commons) Formation - Acts of Union 17071 May 1707 - Acts of Union 18001 January 1801 - Anglo-Irish Treaty 6 December 1922 - Joined the EEC (now the EU)1 January 1973 Area - Total243,610 sq km Population - 2012 estimate 63,705,000 (22nd), Density 255.6/km2 (51st) GDP - (PPP, 2013 estimate) Total $2.378 trillion (8th) GDP - (nominal, 2013 estimate) - Total $2.490 trillion (6th) Currency - Pound sterling (GBP) Time zone -GMT (UTC) - Summer (DST) BST (UTC+1) Date format - dd/mm/yyyy (AD) Drives - on the left Calling code - +44 ISO 3166 code - GB Internet TLD - .uk
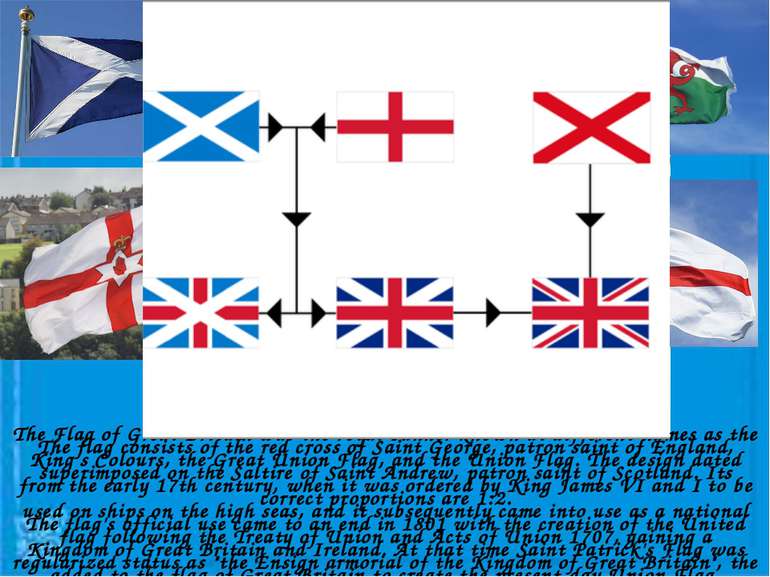
The Flag of Great Britain was the royal banner known at different names as the King's Colours, the Great Union Flag, and the Union Flag. The design dated from the early 17th century, when it was ordered by King James VI and I to be used on ships on the high seas, and it subsequently came into use as a national flag following the Treaty of Union and Acts of Union 1707, gaining a regularized status as "the Ensign armorial of the Kingdom of Great Britain", the newly created state. The flag consists of the red cross of Saint George, patron saint of England, superimposed on the Saltire of Saint Andrew, patron saint of Scotland. Its correct proportions are 1:2. The flag's official use came to an end in 1801 with the creation of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. At that time Saint Patrick's Flag was added to the flag of Great Britain to create the present-day Union Flag.
Publication of an early version in The Gentleman's Magazine, 15 October 1745. The title, on the contents page, is given as "God save our lord the king: A new song set for two voices". "God Save the Queen" (alternatively "God Save the King" during the reign of a male sovereign) is an anthem used in a number of Commonwealth realms, their territories, and the British Crown Dependencies. The words and title are adapted to the gender of the current monarch, i.e. replacing "Queen" with "King", "she" with "he", and so forth, when a king reigns. The author of the tune is unknown, and it may originate in plainchant, but a 1619 attribution to John Bull is sometimes made. Lyrics were written by Henry Carey, 1790
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; born 21 April 1926) is the constitutional monarch of 16 sovereign states, known as the Commonwealth realms, and their territories and dependencies, and head of the 53-member Commonwealth of Nations. She is Supreme Governor of the Church of England and, in some of her realms, carries the additional title of Defender of the Faith.
Arriva London is a bus company operating services in Greater London. It is a subsidiary of Arriva and operates services under contract to Transport for London. It is made up of many previous bus operators including previously independent Grey-Green. Operations are split between two registered companies, Arriva London North Limited and Arriva London South Limited.
Big Ben is the nickname for the great bell of the clock at the north end of thePalace of Westminster in London, and often extended to refer to the clock and the clock tower. The tower is officially known as the Elizabeth Tower (prior to being renamed in 2012 it was known as simply "Clock Tower") to celebrate the Diamond Jubilee of Elizabeth II. The tower holds the largest four-faced chiming clock in the world and is the third-tallest free-standing clock tower.[3] The tower was completed in 1858 and had its 150th anniversary on 31 May 2009, during which celebratory events took place. The tower has become one of the most prominent symbols of the United Kingdom and is often in the establishing shot of films set in London.
The red telephone box, a telephone kiosk for a public telephone designed by Sir Giles Gilbert Scott, was a familiar sight on the streets of the United Kingdom, Malta, Bermuda and Gibraltar. Despite a reduction in their numbers in recent years, the traditional British red telephone box can still be seen in many places throughout the UK, and in current or former British colonies around the world. The colour red was chosen to make them easy to spot. From 1926 onwards, the fascias of the kiosks were emblazoned with a prominent crown, representing the British government. The red phone box is often seen as an iconic British symbol throughout the world.
A leprechaun is a type of fairy in Irish folklore, usually taking the form of an old man, clad in a red or green coat, who enjoys partaking in mischief. Like other fairy creatures, leprechauns have been linked to the Tuatha Dé Danann of Irish mythology. The Leprechauns spend all their time busily making shoes, and store away all their coins in a hidden pot of gold at the end of the rainbow. If ever captured by a human, the Leprechaun has the magical power to grant three wishes in exchange for their release. Popular depiction shows the Leprechaun as being no taller than a small child, with a beard and hat, although they may originally have been perceived as the tallest of the mound-dwellers.
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument in Wiltshire, England, about 2 miles (3.2 km) west of Amesbury and 8 miles (13 km) north of Salisbury. One of the most famous sites in the world, Stonehenge is the remains of a ring of standing stones set withinearthworks. It is in the middle of the most dense complex of Neolithic and Bronze Age monuments in England, including several hundred burial mounds.
Bagpipes are a class of musical instrument, aerophones, using enclosedreeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. Though the Scottish Great Highland bagpipe and Irish uilleann pipes have the greatest international visibility, bagpipes have been played for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, the Caucasus, around the Persian Gulf and in Northern Africa. The term "bagpipe" is equally correct in the singular or plural, although in the English language, pipers most commonly talk of "the pipes", "a set of pipes" or "a stand of pipes".
Christmas is an annual commemoration of the birth of Jesus Christ and a widely observed cultural holiday, celebrated generally onDecember 25 by millions of people around the world. Afeast central to the Christian liturgical year, it closes the Advent season and initiates the twelve days of Christmastide, which ends after the twelfth night.
Saint Patrick's Day is a cultural and religiousholiday celebrated annually on 17 March, the death date of the most commonly-recognised patron saint of Ireland, Saint Patrick. Saint Patrick's Day was made an official Christian feast day in the early seventeenth century and is observed by the Catholic Church, the Anglican Communion (especially the Church of Ireland), the Eastern Orthodox Church and Lutheran Church. The day commemorates Saint Patrick and the arrival of Christianity in Ireland. According to legend, Saint Patrick used the three-leaved shamrock to explain the Holy Trinity to Irish pagans.
Good Friday is a religious holiday, observed primarily by Christians, commemorating the crucifixion of Jesus and his death at Calvary. The holiday is observed during Holy Week as part of the Paschal Triduum on the Friday preceding Easter Sunday, and may coincide with the Jewish observance of Passover. It is also known as Holy Friday, Great Friday,Black Friday, or Easter Friday, though the last term properly refers to the Friday in Easter week.
January 1 is traditionally a religious feast, but since the 1900s has also become an occasion to celebrate the night of December 31, called New Year's Eve. There are fireworks at midnight at the moment the new year arrives (the major one is in Sydney, New South Wales; watchnight services are also still observed by many.
Daniel Radcliffe, Emma Watson and Rupert Grint of the Harry Potter film series at a London premiere
31, 1991, diplomatic relations were established on 10 January 1992. In November 1991 in Kiev, United Kingdom Consulate General opened, and in January 1992 - the Embassy. Embassy of Ukraine in the United Kingdom Ukraine opened in September 1992 in London.
The Governments of Ukraine and the UK have signed an agreement on cooperation in the fields of education, science and culture, which are fundamental instrument industries. This document allows you to represent Ukrainian culture in Britain and vice versa. Ukrainian folk bands are involved in Britain's music festivals, artists of Ukraine can hold exhibitions of their work. In the field of education serving exchanges of scientists, Ukrainian students are studying at UK universities of the two countries entered into cooperation agreements .
HMC Projects gives students and teachers from Central and Eastern Europe an unparalleled opportunity to study for a year in a British school. The programme has nurtured excellent contacts between young people as they advance in their careers and retain a deep understanding of other countries' traditions and culture. To participate in the competition for the scholarship, students are 10 and 11 classes, which at the time of application for the program was 16-17,5 years.
Схожі презентації
Категорії