Презентація на тему:
Natural_disasters_in_the_world
Завантажити презентацію
Natural_disasters_in_the_world
Завантажити презентаціюПрезентація по слайдам:
Monday, September 5, 2005 Typhoon Nabi Japan has been lashed relentlessly by Typhoon Nabi, with nine meter high waves and torrential downpours. It had been classified as a Category 4 storm, the same strength as the recent Hurricane Katrina in the United States, but was later downgraded to Category 3. Flood warnings were issued from north Okinawa to Tokyo. Rain amounts were predicted to be greater than 19 inches (483 millimeters) for Kyushu, Japan's third largest island, and some areas may receive as much as 1 to 2 inches of rain per hour. "Water was almost reaching the second floor. I was really frightened," said a woman in her 50s.
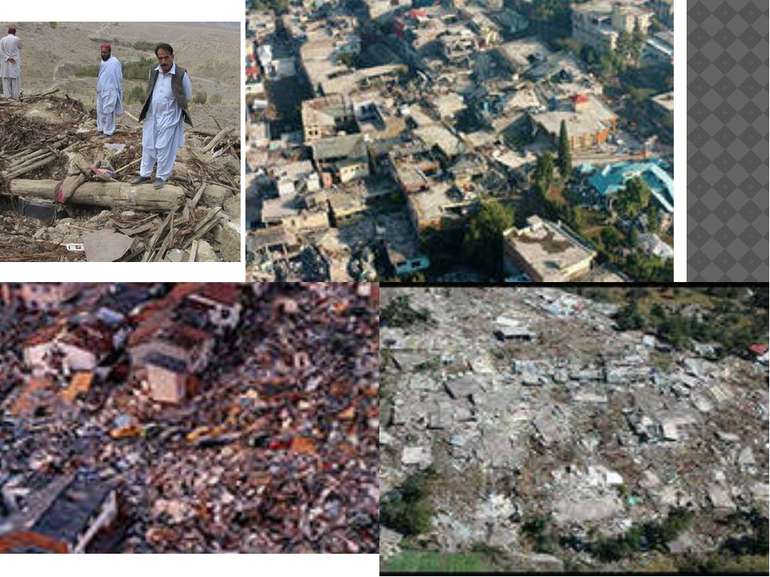
2005 Kashmir earthquake The 2005 Kashmir earthquake was a major earthquake centered in the Pakistan-administered Kashmir near the city of Muzaffarabad, Sehnsa-Kotli Gilgit-Baltistanalso affecting and the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. It occurred at 08:52:37 Pakistan Standard Time (03:52:37 GMT) on 8 October 2005. It registered a moment magnitude of 7.6 making it similar in size to the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, the 1935 Quetta earthquake, the 2001 Gujarat earthquake Well over US$ 5.4 billion (400 billion Pakistani rupees) in aid arrived from all around the world. US Marine and Army helicopters stationed in neighbouring Afghanistan quickly flew aid into the devastated region
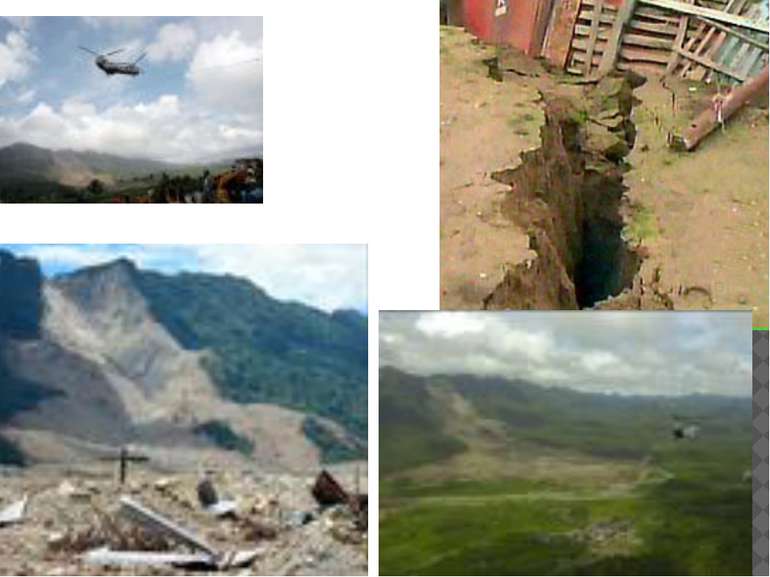
landslide to Guinsaugon's Philippine village On February 17, 2006, a disastrous rockslide-debris avalanche occurred in tropical mountain terrain, on Leyte Island, Central Philippines. Over 1100 people perished when the village of Guinsaugon was overwhelmed directly in the path of the landslide. Tectonic weakening of the failed rock mass had resulted from active strike-slip movements along the Philippine Fault which have been estimated by other workers at 2.5 cm/year. The landslide involved a total volume of 15 Mm3, including significant entrainment from its path, and ran out a horizontal distance of 3800 m over a vertical distance of 810 m, equivalent to a fahrböschung of 12°
Схожі презентації
Категорії