Презентація на тему:
"Education in Canada"
Завантажити презентацію
"Education in Canada"
Завантажити презентаціюПрезентація по слайдам:
The school system of Canada is very much like the one in the USA, but there are certain differences. Education in Canada is general and compulsory for children from 6 to 16 years old, and in some provinces — to 14. It is within the competence of the local authorities, and therefore it may differ from province to province. For example, Newfoundland has an 11-grade system. Some other provinces have 12-grade systems, and Ontario has even a 13-grade system. Grades 1—6 are usually elementary schools, and grades 7—12 are secondary schools.
In some provinces there is a kindergarten year before the first grade. Elementary education is general and basic, but in the junior high school years the students can select some courses themselves. Most secondary schools provide programmes for all types of students. Some of them prepare students for continuing their studies at the university. Vocational schools are separate institutions for those who will not continue their education after secondary schools. There also exist some commercial high schools. Some provinces have private kindergartens and nursery schools for children of pre-elementary age. There also exist Roman Catholic schools and private schools in some provinces. In most provinces private schools receive some form of public support.
Admission to the university in Canada is after high school with specific courses. Getting a degree in law, medicine, dentistry or engineering usually takes 3—4 years of studying. University tuition fees vary among different provinces. All provinces also have public non-university institutions. They are regional colleges, institutes of technology, institutes of applied arts, colleges of agricultural technology and others. Criteria for admission to these institutions are less strict. Regional college Institute of technology Institute of applied arts
The history of education in Canada, as in other Western countries, has involved the growth of formal instruction funded by taxes and supervised by the state. This growth resulted from concern about cultural, moral and political behaviour, the emergence of a wage-labour economy, changing concepts of childhood and the family, and the general reorganization of society into institutions. By the late 20th century, schooling had become part of an institutional network which included hospitals, businesses, prisons, and welfare agencies. Various groups experienced this development in different ways, sometimes by official design and sometimes by their own choice. As a result, there are many histories of Canadian education and important distinctions within the general trends. Prairie Classroom, 1915 Prairie School Coldridge School, circa 1905 (courtesy Saskatchewan Archives Board). Prairie classroom at Bruderheim, Alberta. Prairie schools were to be the vehicles by which immigrants would be assimilated (courtesy Glenbow Archives). School At Canoe Cove, P.E.I. Painting by Robert Harris, oil on canvas. This scene illustrates a Prince Edward Island one-room schoolhouse in the early 1900s, where children of various ages sat together and were instructed by one teacher
The education system in Canada encompasses both publicly-funded and private schools, including: community colleges/ technical institutes,career colleges, language schools, secondary schools, summer camps, universities and university colleges. Education is a provincial responsibility under the Canadian constitution, which means there are significant differences between the education systems of the different provinces. However, education is important to Canadians, and standards across the country are uniformly high.
Every year almost 150,000 international students come to Canada to pursue one or another higher study program. They come from nations all over the globe to pursue an education at Canadian high-schools, colleges and universities. Canadian place great importance on learning, and have developed a first-rate education system with very high standards.
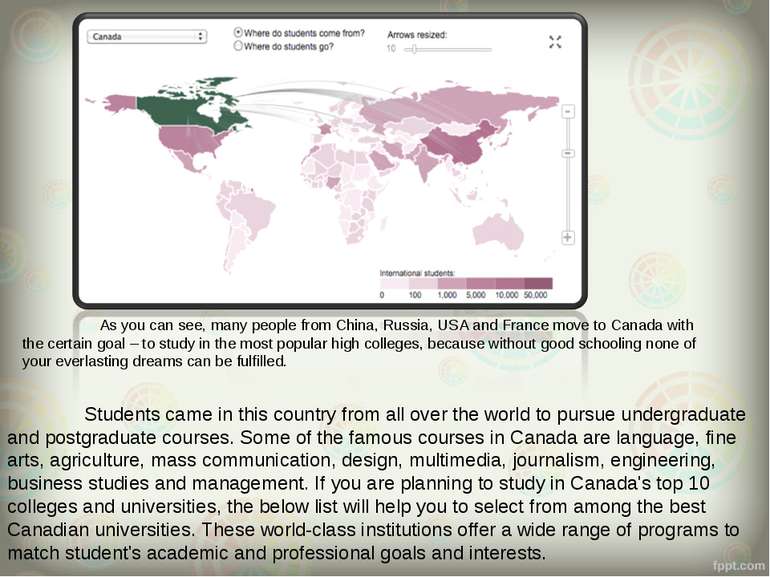
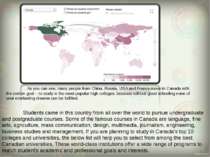
As you can see, many people from China, Russia, USA and France move to Canada with the certain goal – to study in the most popular high colleges, because without good schooling none of your everlasting dreams can be fulfilled. Students came in this country from all over the world to pursue undergraduate and postgraduate courses. Some of the famous courses in Canada are language, fine arts, agriculture, mass communication, design, multimedia, journalism, engineering, business studies and management. If you are planning to study in Canada's top 10 colleges and universities, the below list will help you to select from among the best Canadian universities. These world-class institutions offer a wide range of programs to match student's academic and professional goals and interests.
1. McGill University is a public research university located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1821 during the British colonial era, the university bears the name of James McGill, a prominent Montreal merchant from Glasgow, Scotland and alumnus of Glasgow University, whose bequest formed the beginning of the university. With 21 faculties and professional schools, McGill offers degrees and diplomas in over 300 fields of study, including cultural studies, medicine and law. As of the 2013-2014 school year, McGill was ranked 1st in Canada among all its major universities.
The University of Toronto is a public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, situated on the grounds that surround Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 as King's College, the first institution of higher learning in Upper Canada. Originally controlled by the Church of England, the university assumed the present name in 1850 upon becoming a secular institution. As a collegiate university, it comprises twelve colleges that differ in character and history, each retaining substantial autonomy on financial and institutional affairs.
The University of British Columbia is a public research university in British Columbia, Canada. Founded in 1908 as the McGill University College of British Columbia, the university became independent and adopted its current name in 1915. It is the oldest institution of higher learning in British Columbia and enrolls over 57,000 students at its Vancouver and Okanagan Valley campuses. In 2011, UBC reported the highest entrance requirements for undergraduate admission in Canada
The University of Alberta is a public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford, the first premier of Alberta, and Henry Marshall Tory (McGill University alumni),ts first president. Its enabling legislation is the Post-secondary Learning Act. The university comprises four campuses in Edmonton, the Augustana Campus in Camrose, and a staff centre in downtown Calgary. The original north campus consists of 150 buildings covering 50 city blocks on the south rim of the North Saskatchewan River valley
Queen's University at Kingston is a public research university located in Kingston, Ontario, Canada. Founded on 16 October 1841, the university predated the founding of Canada by 26 years. Queen's holds more than 1,400 hectares (3,500 acres) of land throughout Ontario and owns Herstmonceux Castle in East Sussex, England. Queen's is organized into ten undergraduate, graduate and professional faculties and schools. The Church of Scotland established Queen's College in 1841 with a royal charter from Queen Victoria.
Presentation by Anton Stavruk, Revenko Dmytro, Sereda Katerina, Yedyharyan Karina, Levishenko Ludmila, yo yo !!!
Схожі презентації
Категорії