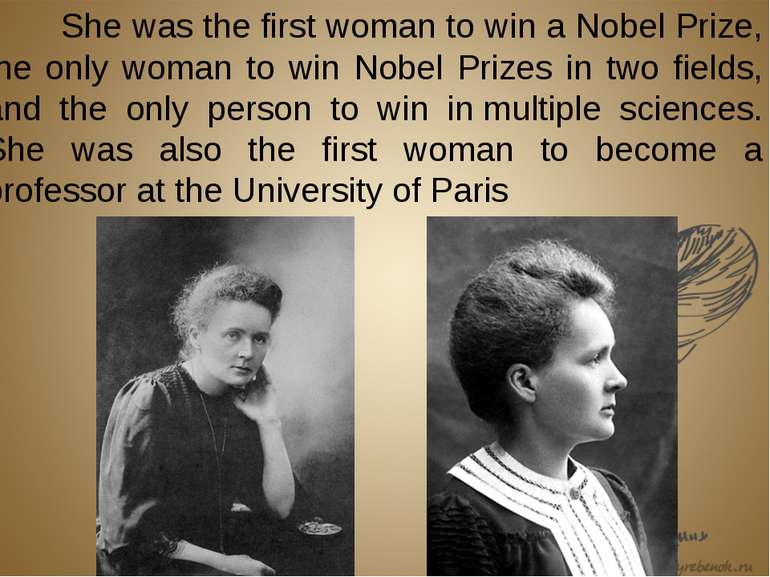Презентація на тему:
"Marie Sklodowska-Curie "
Завантажити презентацію
"Marie Sklodowska-Curie "
Завантажити презентаціюПрезентація по слайдам:
Early years Maria Skłodowska was born in Warsaw, in the Russian partition of Poland, on 7 November 1867, the fifth and youngest child of well-known teachers .
New life in Paris In late 1891 she left Poland for France. There she studied at the University of Paris. Marie studied during the day and tutored evenings, barely earning her keep. In 1893 she was awarded a degree in physics and began work in an industrial laboratory of Professor Gabriel Lippmann.
Scientific career Marie had begun her scientific career in Paris with an investigation of the magnetic properties of various steels, commissioned by the Society for the Encouragement of National Industry That same year Pierre Curie entered her life; it was their mutual interest in natural sciences that drew them together.
Marriage A contemporary quip would call Marie, "Pierre's biggest discovery." On 26 July 1895 they married in a civil union , neither wanted a religious service. In Pierre, Marie had found a new love, a partner, and a scientific collaborator on whom she could depend.
New elements In July 1898 Curie and her husband published a joint paper announcing the existence of an element which they named "polonium", in honour of her native Poland. On 26 December 1898, the Curies announced the existence of a second element, which they named "radium", from theLatin word for "ray In the course of their research, they also coined the word "radioactivity"
Nobel Prizes In December 1903, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awarded Pierre Curie, Marie Curie, and Henri Becquerel the Nobel Prize in Physics. International recognition for her work had been growing to new heights, with the result that the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences honored her a second time, with the 1911 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Death Curie visited Poland for the last time in early 1934. A few months later, on 4 July 1934, she died from aplastic anemia , believed to have been contracted from her long-term exposure to radiation
She was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, the only woman to win Nobel Prizes in two fields, and the only person to win in multiple sciences. She was also the first woman to become a professor at the University of Paris
Схожі презентації
Категорії