Презентація на тему:
"Henri Matisse"
Завантажити презентацію
"Henri Matisse"
Завантажити презентаціюПрезентація по слайдам:
Henri-Émile-Benoît Matisse was a French artist, known for his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known primarily as a painter.
Matisse was born in Le Cateau-Cambrésis, in the Nord department in northern France, the oldest son of a prosperous grain merchant. He grew up in Bohain-en-Vermandois, Picardie, France. In 1887 he went to Paris to study law, working as a court administrator in Le Cateau-Cambrésis after gaining his qualification. He first started to paint in 1889, after his mother brought him art supplies during a period of convalescence following an attack of appendicitis. Initially he painted still-lifes and landscapes in a traditional style, at which he achieved reasonable proficiency. Early life and education
With the model Caroline Joblau, he had a daughter, Marguerite, born in 1894. In 1898 he married Amélie Noellie Parayre; the two raised Marguerite together and had two sons, Jean (born 1899) and Pierre (born 1900). Marguerite and Amélie often served as models for Matisse.
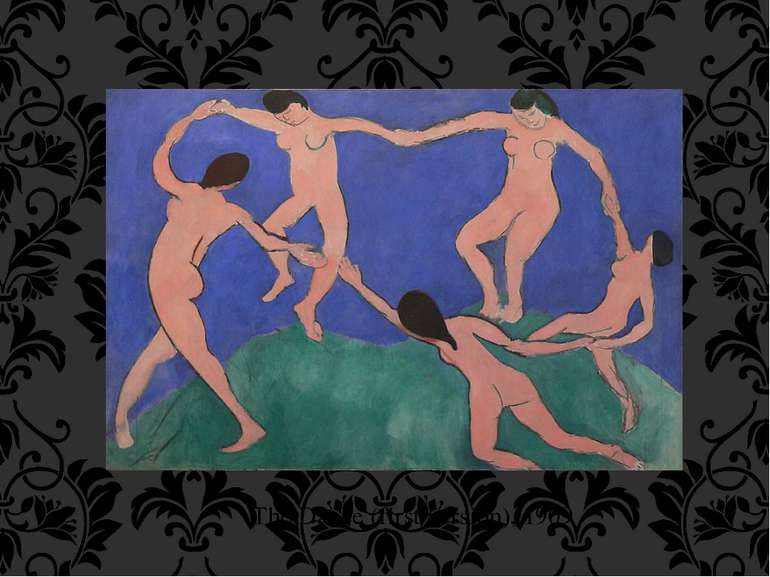
Fauvism as a style began around 1900 and continued beyond 1910, the movement as such lasted only a few years, 1904–1908, and had three exhibitions. The leaders of the movement were Matisse and André Derain. Matisse's first solo exhibition was at Ambroise Vollard's gallery in 1904, without much success. The decline of the Fauvist movement after 1906 did not affect the career of Matisse; many of his finest works were created between 1906 and 1917. Fauvism
Selected works: Paris, 1901–1910 A Glimpse of Notre-Dame in the Late Afternoon, 1902 Madras Rouge, The Red Turba, 1907,
Around April 1906 he met Pablo Picasso, who was 11 years younger than Matisse. The two became lifelong friends as well as rivals and are often compared; one key difference between them is that Matisse drew and painted from nature, while Picasso was much more inclined to work from imagination. The subjects painted most frequently by both artists were women and still life, with Matisse more likely to place his figures in fully realised interiors. Gertrude Stein, Académie Matisse, and the Cone sisters
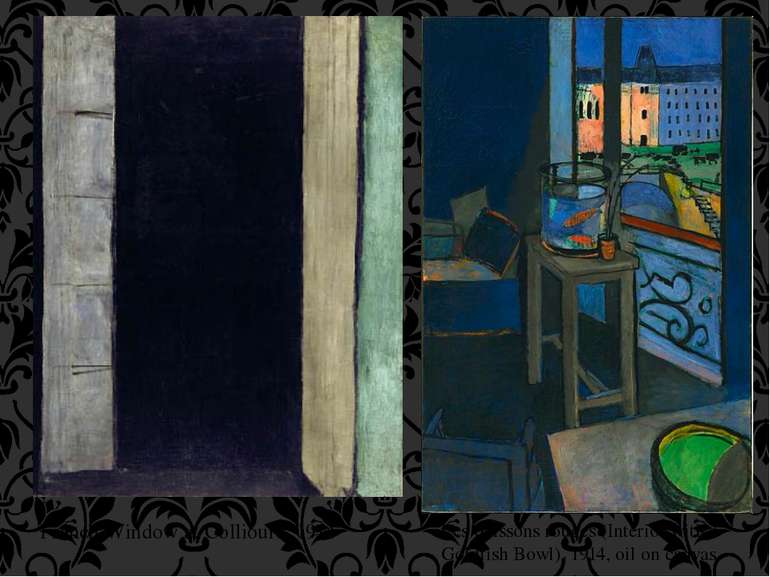
Selected works: Paris, 1910–1917 View of Notre-Dame, 1914 Auguste Pellerin II, 1916-17, oil on canvas
French Window at Collioure, 1914 Les poissons rouges (Interior with a Goldfish Bowl), 1914, oil on canvas
n 1917 Matisse relocated to Cimiez on the French Riviera, a suburb of the city of Nice. His work of the decade or so following this relocation shows a relaxation and a softening of his approach. This "return to order" is characteristic of much art of the post-World War I period, and can be compared with the neoclassicism of Picasso and Stravinsky, and the return to traditionalism of Derain. His orientalist odalisque paintings are characteristic of the period; while this work was popular, some contemporary critics found it shallow and decorative. In the late 1920s Matisse once again engaged in active collaborations with other artists. He worked with not only Frenchmen, Dutch, Germans, and Spaniards, but also a few Americans and recent American immigrants. After Paris
He and his wife of 41 years separated in 1939. In 1941, he underwent surgery in which a colostomy was performed. Afterwards he started using a wheelchair, and until his death he was cared for by a Russian woman, Lydia Delektorskaya, formerly one of his models. In the 1940s he also worked as a graphic artist and produced black-and-white illustrations for several books and over one hundred original lithographs at the Mourlot Studios in Paris. The war years
In 1951 Matisse finished a four-year project of designing the interior, the glass windows and the decorations of the Chapelle du Rosaire de Vence, often referred to as the Matisse Chapel. Last years
Matisse died of a heart attack at the age of 84 in 1954. He is interred in the cemetery of the Monastère Notre Dame de Cimiez, near Nice. Last years
Схожі презентації
Категорії