Презентація на тему:
Executive branch in the USA
Завантажити презентацію
Executive branch in the USA
Завантажити презентаціюПрезентація по слайдам:
The Executive Branch is headed by the President and the Vice President. In addition, it includes the executive departments, which deal with general topics, and the heads of departments, who are known as Secretaries. Each Department, in turn, is divided into a number of bodies, which are known as agencies, services, commissions, councils, bureaus, authorities, offices, administrations, and boards.
The President The President is the highest elected official in the United States. The Constitution grants the President a numbers of powers, including: to implement laws passed by Congress. Representing the United States in foreign affairs. Command of the armed forces. Veto power over bills passed by both houses of Congress. Congress can only override a presidential veto by a 2/3 vote. Nominating Supreme Court justices, executive officials, ambassadors and other public officers. Removing high-level executive officers at any time and for any reason. The President's power to remove lower-level executive officials may be limited by Congress, however. Pardoning any person who has been convicted of a crime, except impeachment and civil contempt.
If the President vacates office for any reason whatsoever, the Vice President becomes President. After the Vice President, the line of succession is as follows: Speaker of the House of Representatives President pro tempore of the Senate Secretary of State Secretary of the Treasury Secretary of Defense Attorney General (Department of Justice) Secretary of the Interior Secretary of Agriculture Secretary of Commerce Secretary of Labor Secretary of Health and Human Services Secretary of Housing and Urban Development Secretary of Transportation Secretary of Energy Secretary of Education Secretary of Veterans Affairs Secretary of Homeland Security
The Vice President The Vice President's only executive function in the Constitution is to become President in the event that the President dies or is incapacitated. The 25th Amendment provides that this may occur when: "the President transmits to the President pro tempore of the Senate and the Speaker of the House of Representatives his written declaration that he is unable to discharge the powers and duties of his office, and until he transmits to them a written declaration to the contrary;" or "the Vice President and a majority of either the principal officers of the executive departments or of such other body as Congress may by law provide, transmit to the President pro tempore of the Senate and the Speaker of the House of Representatives their written declaration that the President is unable to discharge the powers and duties of his office." Additionally, "whenever there is a vacancy in the office of the Vice President, the President shall nominate a Vice President who shall take office upon confirmation by a majority vote of both Houses of Congress." In practice, the Vice President often takes an active role in policy making. The Vice President also serves as president of the Senate, but cannot vote except to break a tie.
Elections Each state is entitled to choose a number of Electors equal to the number of Representatives and Senators it elects to Congress. Thus, a state will choose no less than three electors- two for the Senators, and one for the minimum of one Representative. The state may choose its Electors in any way it pleases. However, all the states allow the people to choose all Electors. If, however, no candidate received a majority, then the House of Representatives would choose one of the top five candidates as President. In voting for President, each state casts one block vote. In any case, whichever other candidate holds the greatest number of votes other than the candidate elected President becomes Vice President. In case of a tie for second-place, the Senate elects the Vice President.
Executive departments At present, there are fifteen executive departments. They are the departments of: Department of Agriculture (USDA) Department of Commerce (DOC) Department of Defense (DOD) Department of Education (ED) Department of Energy (DOE) Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) Department of Justice (DOJ) Department of Labor (DOL) Department of State (DOS) Department of the Interior (DOI) Department of the Treasury Department of Transportation (DOT) Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Each department is subdivided into a number of agencies, bureaus and other divisions.
Executive agencies In addition to the Cabinet departments, there are certain independent bodies which are not part of any department, but report directly to the Executive Office of the President. These include: Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Office of Management and Budget (OMB) Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP) Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR)
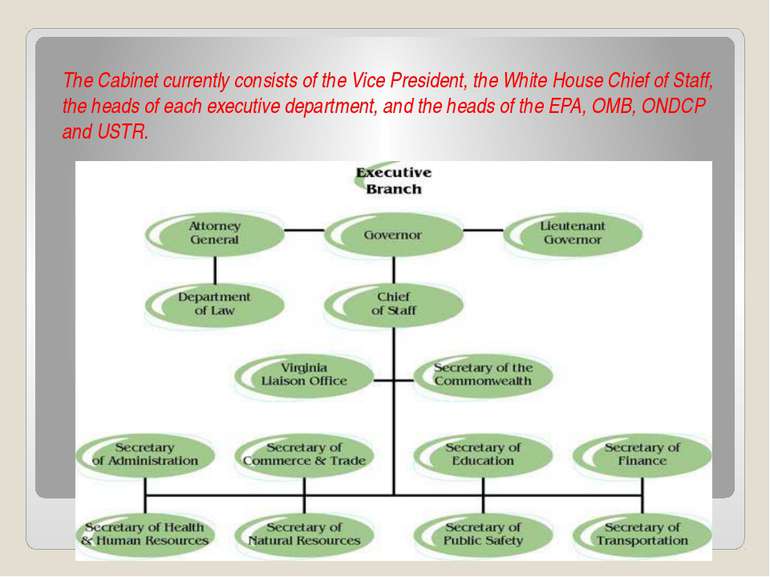
The Cabinet currently consists of the Vice President, the White House Chief of Staff, the heads of each executive department, and the heads of the EPA, OMB, ONDCP and USTR.
Схожі презентації
Категорії